Dental emergencies can affect anyone at any time. Emergencies can cause severe pain, distress and frustration regarding your dental and oral health. If left untreated, an emergency can become an even more insidious problem, requiring additional work and even surgery.
WHAT IS CONSIDERED A DENTAL EMERGENCY?
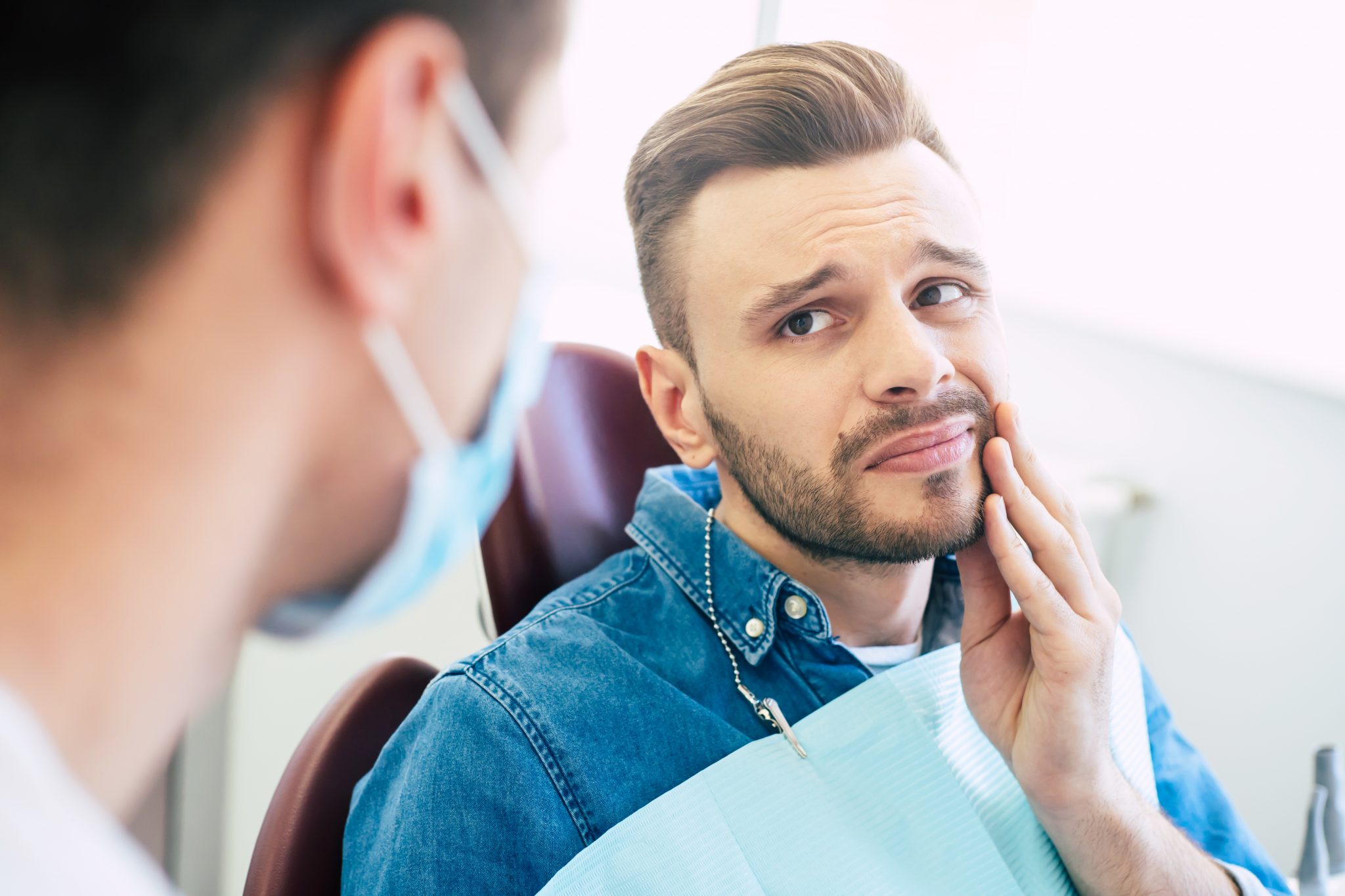
Most common dental emergency is Toothache. Most Toothache happens due to big decay (cavity) that may lead to tooth abscess. Sometimes it can occur due to periodontal (gum) abscess where you haven’t had a cleaning done for a long time. Other common dental emergencies are broken or fractured tooth and knocked out tooth.
WHAT DO I DO DURING A DENTAL EMERGENCY?
Try to stay calm and do not panic.
Most dental emergencies are extremely painful so first, take some pain medicines such as Advil or Tylenol. Make sure you’re not allergenic to the pain medicine you’re taking. Advil contains 200mgs of Ibuprofen, so you can take up to 3-4 tablets (600-800mgs Ibuprofen) at the same time, do not exceed more than 3200mgs in 24 hrs.
Rinse with warm salt water and put some ice pack on cheek closest to broken tooth or abscess area.
Avoid eating too hot, too hard or too spicy food, and chew on the other side of your mouth. Be gentle with brushing and flossing in that area.
Call your dentist immediately to schedule an appointment ASAP. If you have a huge swelling, excessive bleeding at night or during weekends and you can’t see your regular dentist, then go to the nearest Emergency Room.
HOW DO I FIND AN EMERGENCY DENTIST?
It is very crucial to find a skilled dentist who can get you out of pain right away and treat you like a family member. While looking for a dentist, look for their reviews, and ask what latest technologies are at the practice.
exploring the child’s bite or observing the position of the maxillary bones with each other and in the whole. Although the child’s rash and bite are correct, it is important to perform annual checkups to follow the entire process of dental replacement in the oral cavity. Children should go to the dentist or specialist for the first time, to the pediatric dentist, every year since the first teeth erupt (at 6 months). These appointments are important to be able to diagnose with time any series of changes in the oral cavity that may go unnoticed by the child’s parents.
HOW DO I PREVENT A DENTAL EMERGENCY?
The best way to prevent a dental emergency is to see your dentist regularly. The recommended appointment schedule is a check up every 6 months. Other ways dental emergencies can be prevented are:
- Wearing a mouth guard during sports or physical activities.
- Avoid eating excessive hard food and ice cubes.
- Do not try to open objects (bottles, cans, packaging, etc.) with your teeth; it may turn into very expensive and painful endeavor.